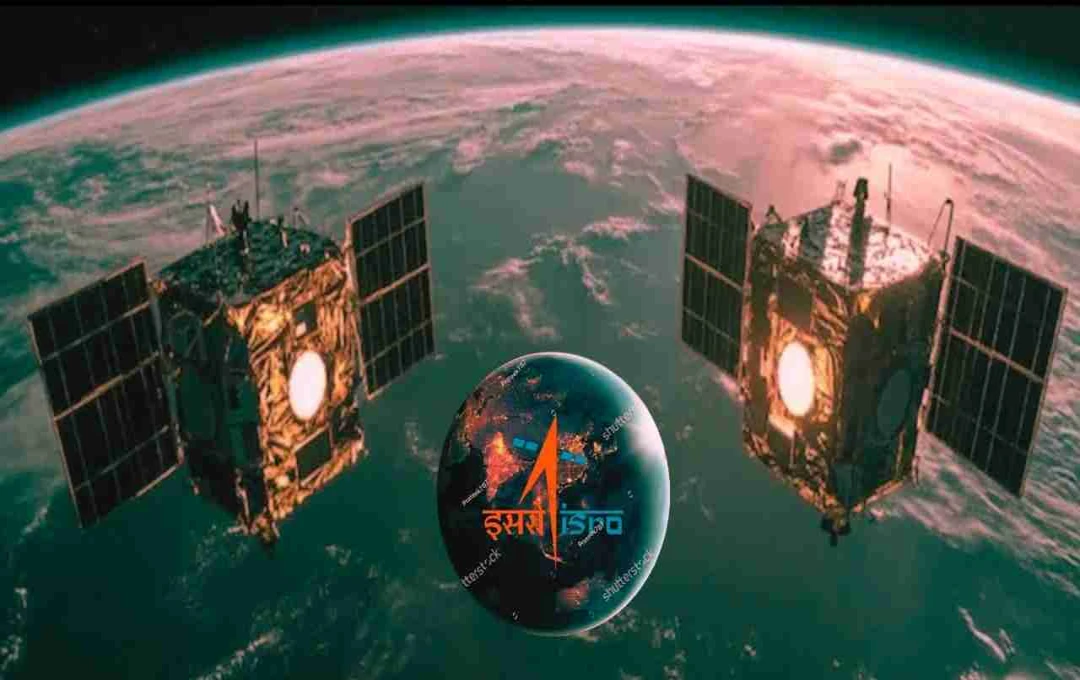
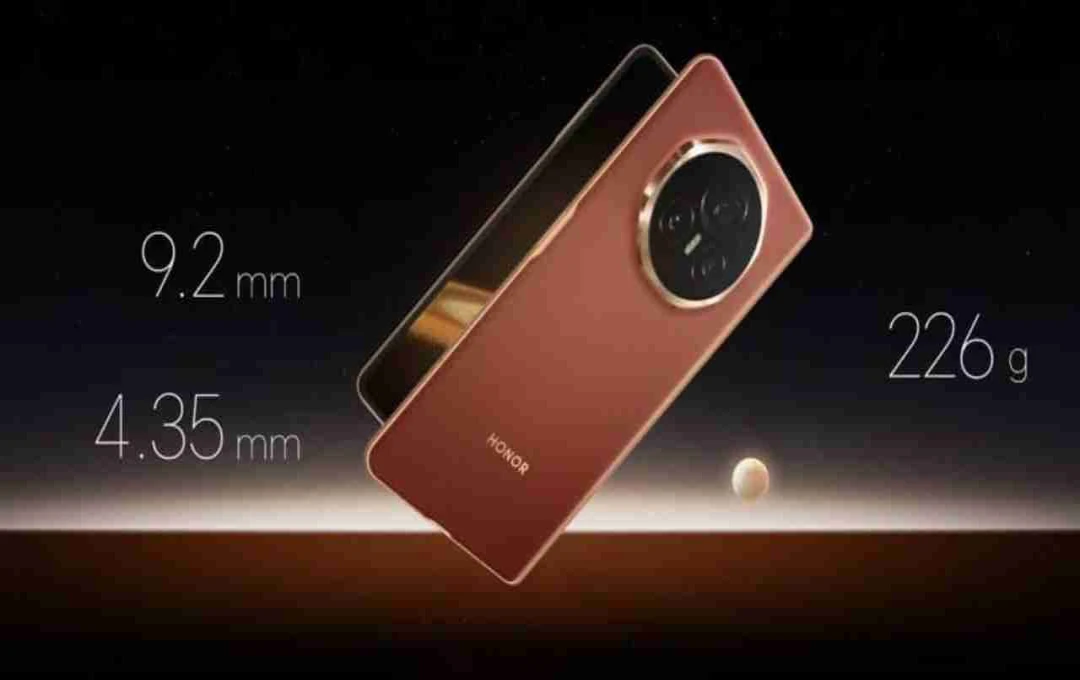
ISRO achieves a significant milestone by successfully docking chaser and target satellites under the SPADEX mission, paving the way for advancements in future space technology.
India's space agency, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation), has achieved another significant feat. ISRO has successfully docked two satellites in space for a second time, a remarkable achievement opening numerous new possibilities for India's future space endeavors.
This ISRO mission is known as SPADEX (Space Docking Experiment). The mission involved launching two small satellites – Chaser and Target – with the objective of autonomously docking with each other.
What is 'Docking' and why is it significant?
Docking is a technique where two spacecraft or satellites connect in space. This is a highly complex operation, as space involves high velocities, the absence of gravity, and requires precise timing.
Consequently, this technology is possessed by only a select few nations. India has now joined the ranks of countries mastering the technology of satellite docking in space.
What is ISRO's SPADEX mission?
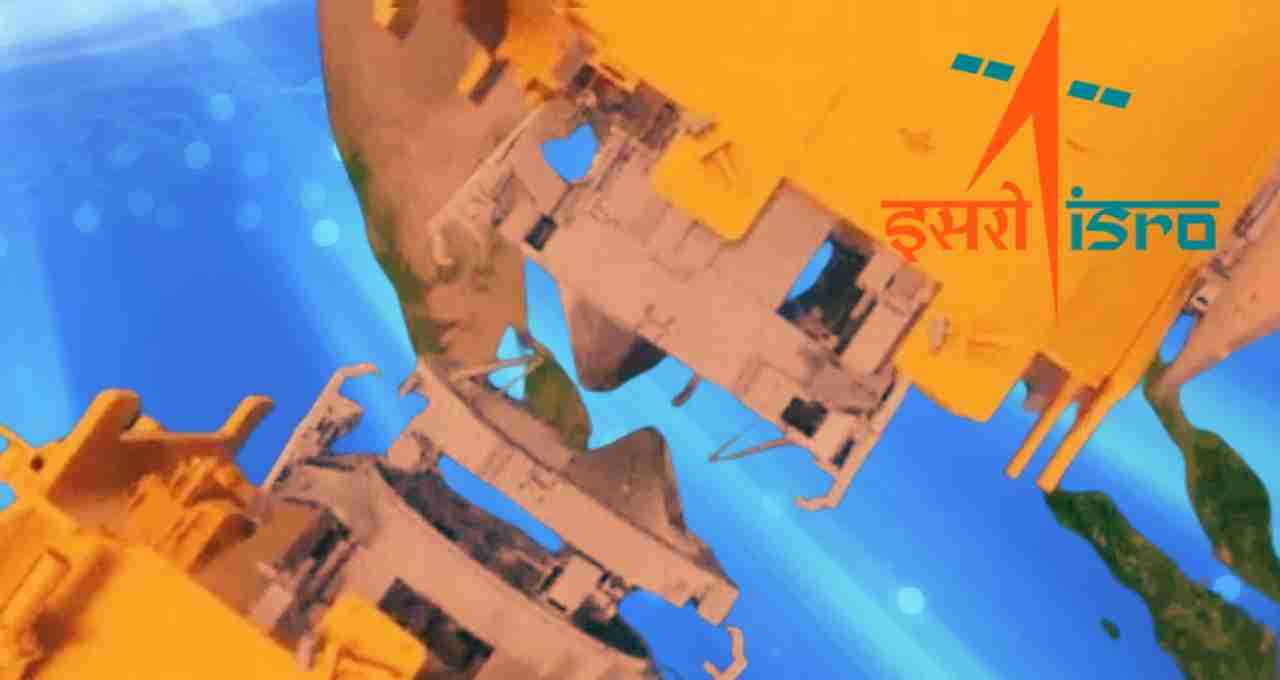

ISRO's SPADEX mission, short for Space Docking Experiment, involved sending two small satellites – Chaser and Target – into space to connect with each other.
ISRO aimed to test whether India's space technology is capable of autonomously docking two satellites in space.
ISRO's second successful attempt
ISRO conducted a similar experiment a few months prior, where the satellites docked at a distance of 3 meters. However, that attempt involved some manual intervention.
This second attempt presented a greater challenge:
• The satellites docked from a distance of 15 meters.
• The entire process was autonomous, with no human intervention.
• The docking was completely automated, a significant technological achievement.
Power transfer also achieved post-docking
Beyond successful docking, ISRO also achieved successful power transfer between the two satellites. This involved one satellite providing energy to the other, and vice-versa.
This experiment demonstrates the potential for one satellite to recharge another in case of battery depletion. ISRO reported that this power transfer lasted approximately 4 minutes, during which heater elements were also operated.
Why is this technology crucial for India?
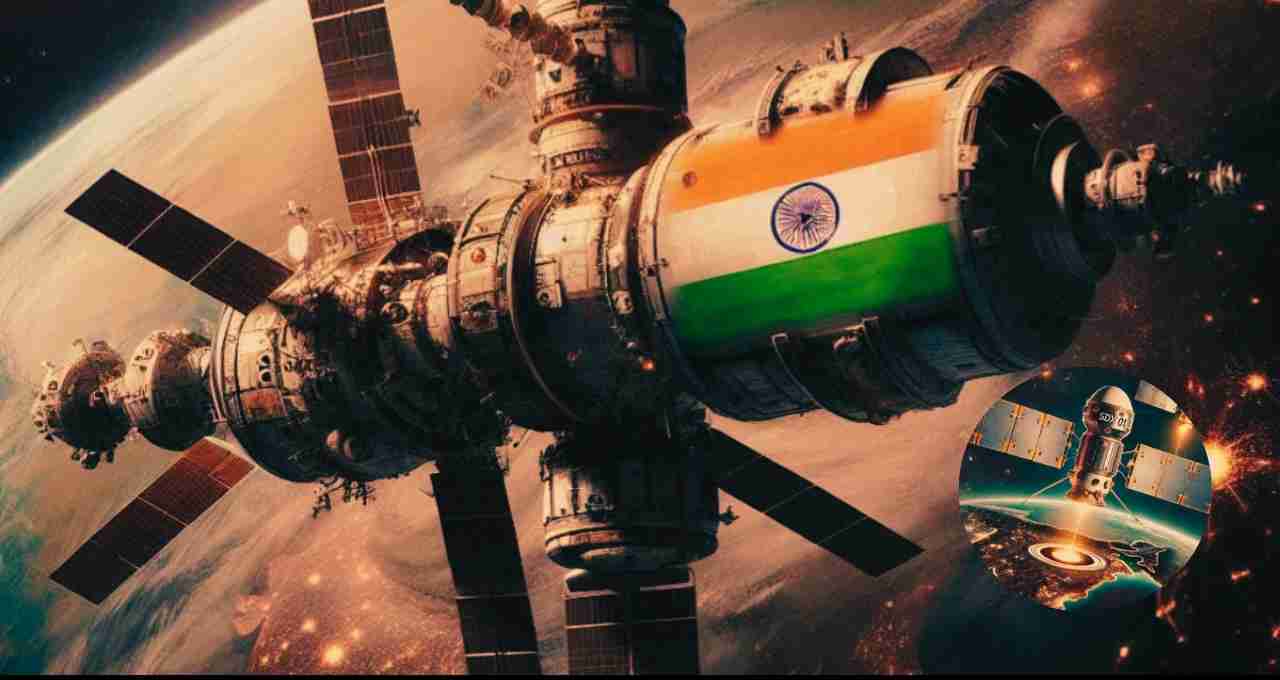

This ISRO mission is more than just a technical experiment; it is crucial for India's future space missions. Here's why:
1. Aids in space station construction – This technology is essential for India to potentially build its own space station, similar to those operated by the US and Russia.
2. Enables in-space satellite repair and recharging – This technology allows for the repair or recharging of malfunctioning or depleted satellites in space.
3. Supports Gaganyaan and interplanetary missions – Docking technology is vital for future Indian missions to send humans to the moon or Mars.
Mission development
The SPADEX mission was developed by ISRO after extensive planning and technological advancements. The small satellites were specifically designed for docking.
These satellites were equipped with sensors, cameras, and navigation systems to enable mutual recognition and precise docking.
Future plans
ISRO's chairman indicated that work on future plans will commence following this experiment. This suggests that ISRO may soon plan more advanced docking missions and utilize this technology in larger, crew-based missions.