Eyes are the most important and sensitive organs of our body. They are the gateway to perceiving and understanding the world, yet we often neglect their care until a serious problem arises. Weakening eyesight is becoming a common problem, which can take a serious turn if not addressed timely. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the reasons behind deteriorating eyesight, its symptoms, and how we can improve it.
Major Causes of Weakening Eyesight
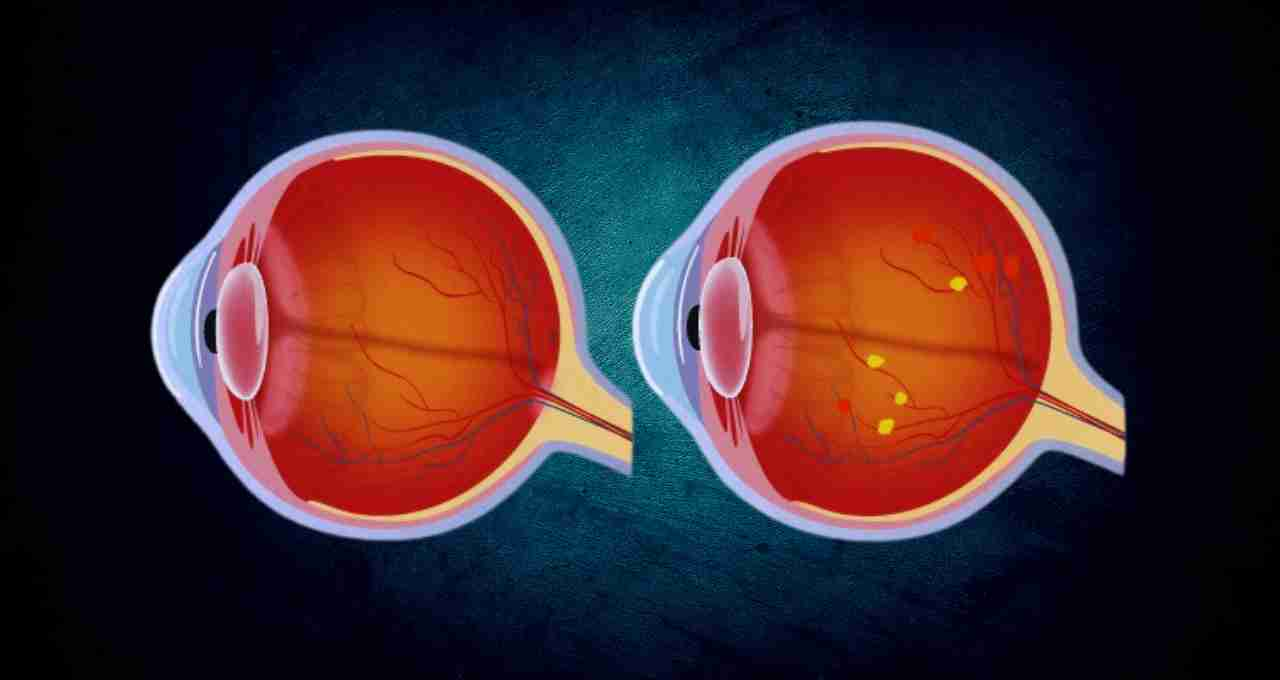
Several factors can contribute to decreased eyesight, some natural and some lifestyle-related.
- Cataracts: Cataracts are a condition where the eye's lens gradually becomes cloudy. This leads to blurry vision and faded colors. While it commonly occurs with age, diabetes and prolonged sun exposure can accelerate its onset.
- Glaucoma: This is a serious eye disease where increased pressure inside the eye damages the optic nerve. This leads to vision loss and, if left untreated, can cause blindness.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes causes damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to impaired vision. This condition arises from poor blood sugar control.
- Macular Degeneration: This age-related condition affects the central vision (macula), causing difficulty in reading and facial recognition.
- Poor Lifestyle and Screen Time: In today's digital age, excessive screen time (mobile phones, computers, and TV) strains the eyes, leading to weakened vision. Nutritional deficiencies and smoking also contribute to deteriorating eyesight.
Symptoms of Weakening Eyesight
If you experience the following symptoms, they may indicate a problem with your eye health:
- Blurry vision, especially difficulty seeing near or distant objects clearly
- Eye strain or fatigue while reading or writing
- Burning, itching, or redness in the eyes
- Persistent headaches and heaviness in the eyes
- Sudden dimming of vision or vision loss
- Excessive watering or tearing of the eyes
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult an ophthalmologist immediately.
Essential Measures for Eye Care
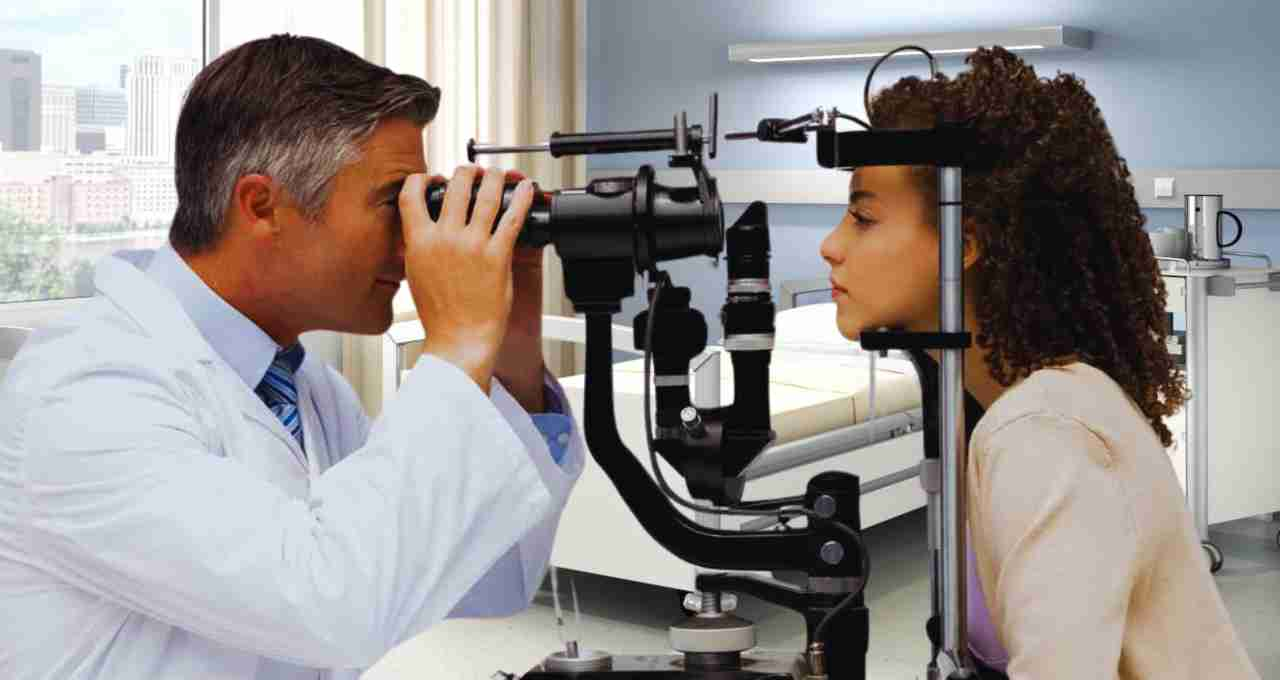

- Regular Eye Checkups: People with diabetes and high blood pressure should undergo regular eye examinations. Even in old age, a yearly checkup with an ophthalmologist is recommended.
- Reduce Screen Time: Limit the use of mobile phones, computers, and television. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds to rest your eyes.
- Maintain a Nutritious Diet: Consume foods rich in Vitamins A, C, E, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids to improve eyesight. Carrots, spinach, fish, nuts, and seasonal fruits are particularly beneficial.
- Sun Protection: Wear sunglasses with UV protection to shield your eyes from harmful rays.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is detrimental to eye health and contributes to several serious eye diseases.
- Eye Exercises: Perform simple eye exercises daily, such as rolling your eyes and focusing on near and distant objects, to strengthen eye muscles.
- Get Enough Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining healthy eyes. It allows the eyes to rest and rejuvenate.
When to Consult a Doctor?
Never ignore persistent eye irritation, pain, blurry vision, or sudden vision loss. Headaches accompanied by eye heaviness or pain may indicate a serious condition. Do not delay; consult a qualified ophthalmologist immediately for prompt treatment and to protect your vision.
Eyes are the light of our lives and should never be taken lightly. Weakening eyesight is not a trivial problem; it can be a serious challenge to your lifestyle and health. Regular eye checkups, a healthy diet, and controlled screen time are essential.