Recurring knee pain can be a sign of several serious conditions, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or calcium deficiency in bones. Experts say that managing weight, consuming a calcium-rich diet, regular exercise, and adopting correct sitting and standing postures can help in prevention.
Pain in knees: Persistent knee pain is not merely a consequence of aging or fatigue; it can be a symptom of conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or bone weakness. According to Dr. Bhavuk Garg, Orthopedic Professor at AIIMS, this issue is becoming common among youth and women as well. Along with pain, symptoms such as swelling, stiffness, difficulty in movement, and clicking sounds may appear. Timely diagnosis and medical consultation are crucial.
Symptoms accompanying knee pain
Along with persistent knee pain, several other symptoms are also observed. These include swelling in the knees, feeling of stiffness, difficulty climbing and descending stairs, clicking sounds from the knees when walking, and sleep disturbance due to pain. Some people also experience burning sensation, warmth, or redness in the knees. All these symptoms can indicate inflammation, injury, or infection. Therefore, knee pain should not be taken lightly.
Causes of recurring pain
Dr. Bhavuk Garg, Professor in the Orthopedic Department at AIIMS, explains that recurring knee pain can be linked to several conditions. The most common cause is osteoarthritis. In this condition, the cartilage between the bones begins to wear down, increasing pain. This disease is more prevalent with age, but nowadays, it is also observed in young people due to lifestyle factors and obesity.
Furthermore, rheumatoid arthritis is also a common cause. This is an autoimmune disease where the body's immunity starts attacking its own bones and joints. This can lead to increased swelling, stiffness, and persistent pain.
In some cases, gout can also cause knee pain. In this condition, an increase in uric acid in the body leads to the formation of crystals in the joints, causing severe pain. Additionally, recurring knee pain can also result from calcium deficiency in bones, injury, overweight, or habits like standing for prolonged periods.
When is it necessary to get checked?
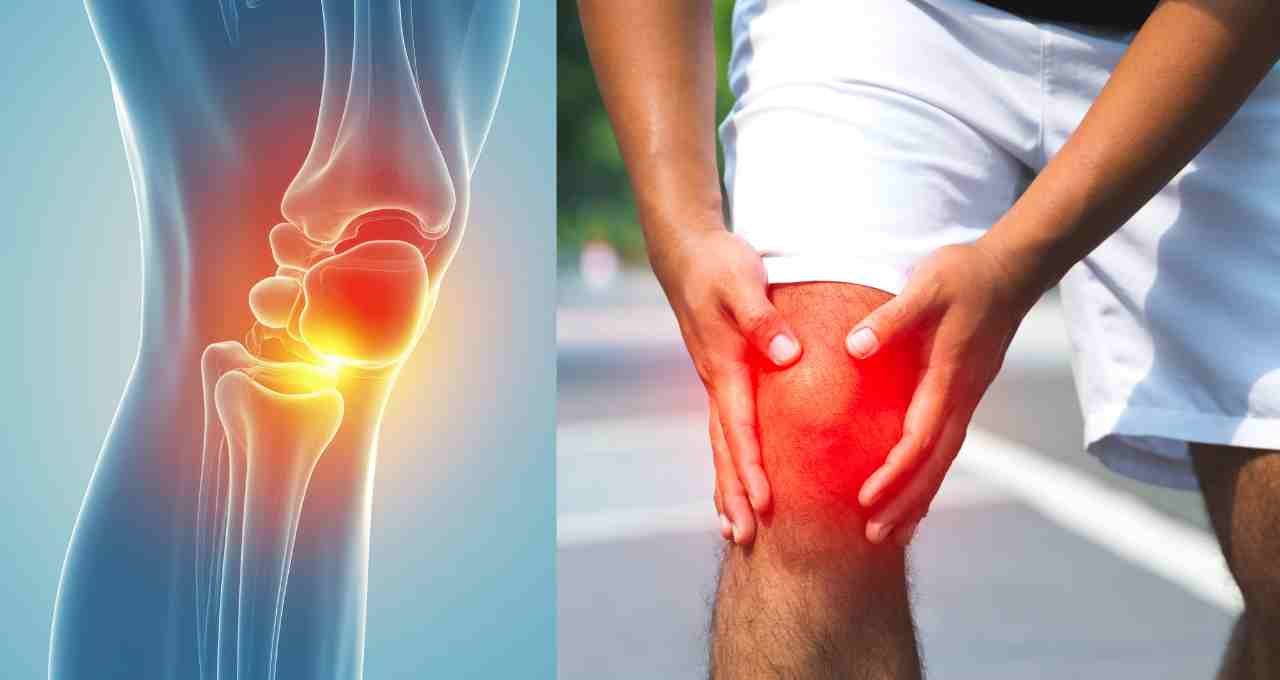
If knee pain persists continuously or returns periodically, timely examination is crucial. Delayed treatment can exacerbate the problem and affect mobility. Experts state that complaints such as swelling, stiffness, and redness accompanying the pain should not be ignored.
Preventive measures
Controlling weight and avoiding being overweight are important for knee health. Consuming a healthy and calcium-rich diet enhances bone strength. Daily light exercises or yoga strengthen the joints. Adopting correct sitting, standing, and walking postures also helps in reducing pain. Using knee caps or support when needed can be beneficial.















