Calcium is a crucial nutrient for our bodies, essential not only for maintaining b bones and teeth but also for regulating muscle contractions, heartbeat, and nervous system functions. Unfortunately, a significant number of people today suffer from calcium deficiency—often without realizing it.
A calcium deficiency gradually impacts various parts of the body. This article will explore the potential health problems associated with calcium deficiency and the symptoms to watch out for.
Why is Calcium So Important?
Calcium's importance extends beyond b bones and teeth. It's vital for numerous bodily processes, including muscle contraction, regulating heartbeat, transmitting nerve signals, and blood clotting.
Ninety-nine percent of the body's calcium resides in bones and teeth, while the remaining 1% remains active in the blood and tissues, driving metabolic functions.
Muscle Cramps and Stiffness
Muscle twitching or cramping is a common and early symptom of calcium deficiency.
Sudden stiffness or pain in the legs, thighs, or lower back, even without strenuous activity, may indicate insufficient calcium intake. This is often more pronounced at night, potentially disrupting sleep.
Bone Pain and Increased Fracture Risk
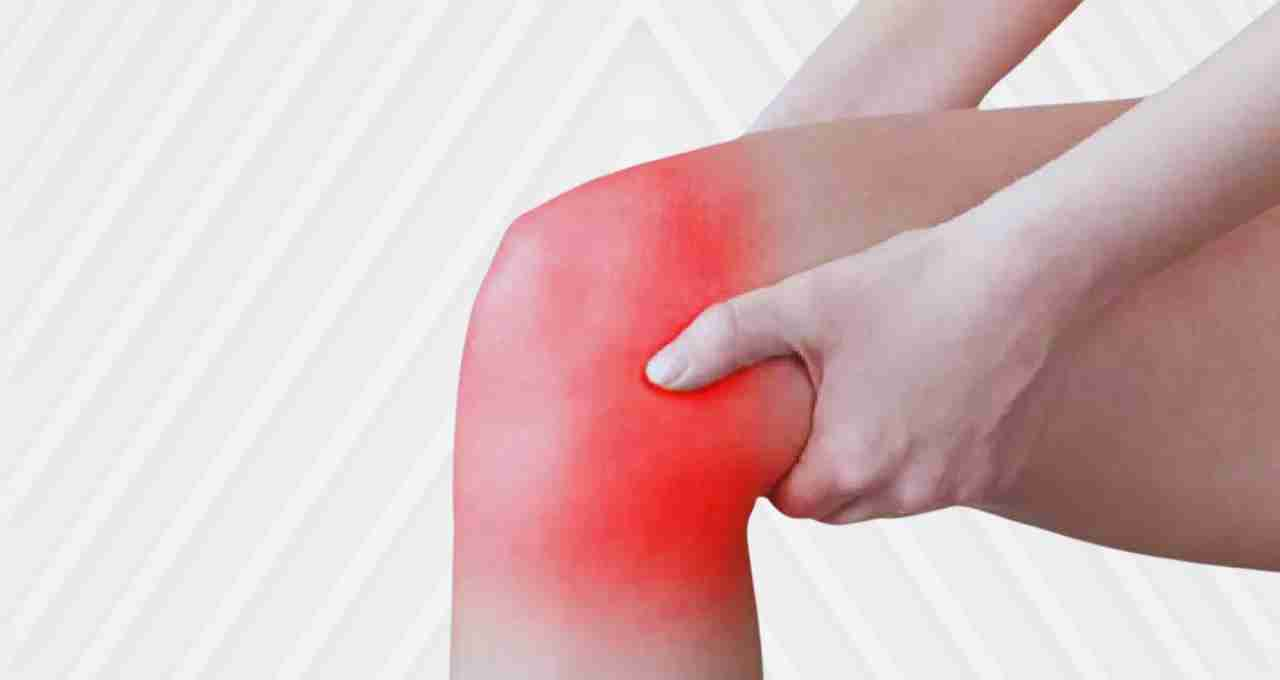
Bones are the body's largest calcium reservoir. In calcium deficiency, the body begins drawing calcium from bones to meet its needs, weakening them.
Prolonged calcium deficiency increases the risk of bone-related diseases like osteopenia or osteoporosis, leading to increased bone fragility and fractures from even minor injuries.
Impact on Hair and Skin Health
Calcium deficiency can also affect your appearance.
- Hair may become dry and brittle.
- Increased hair loss.
- Dry skin and rashes may appear.
Don't ignore persistent dry skin or dulling hair.
Weak and Brittle Nails
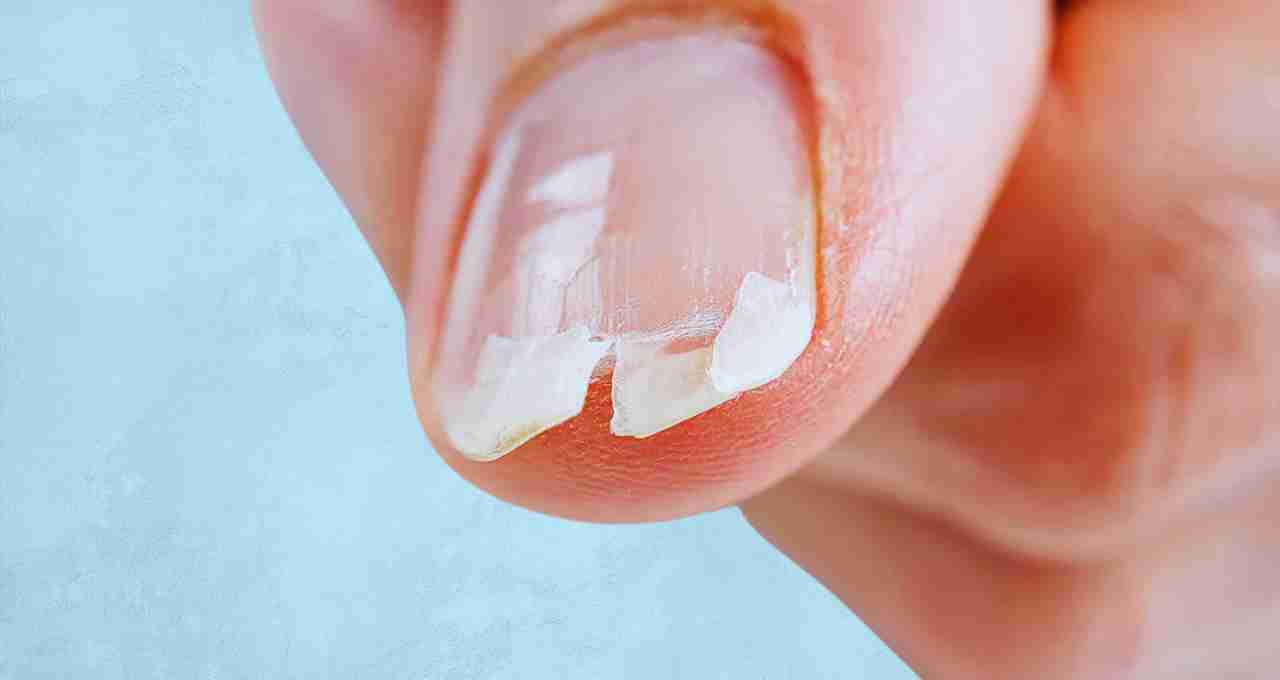
Cracked or frequently breaking nails can also signal calcium deficiency. Nails may also yellow or lose their shine. This is not merely a cosmetic issue but a warning sign of nutritional inadequacy.
Fatigue and Weakness
Calcium plays a crucial role in the body's muscular and energy systems. Deficiency can lead to:
- Fatigue throughout the day
- Shortness of breath with minimal exertion
- Difficulty concentrating
- Insomnia
These symptoms are often overlooked, but timely medical evaluation is crucial.
Dental Problems
Calcium deficiency affects tooth strength. In children, it can hinder tooth development, while adults may experience loose teeth, gum inflammation, or premature tooth loss.
Who is at Higher Risk of Calcium Deficiency?

- Women, especially during pregnancy or menopause
- The elderly, whose bones are already weaker
- Vegetarians with low dairy intake
- Lactose-intolerant individuals who cannot consume milk
- People with kidney or thyroid conditions
Remedies for Calcium Deficiency
- Incorporate calcium-rich foods: Milk, cheese, yogurt, millet, spinach, broccoli, dried figs, sesame seeds, almonds, etc.
- Consume Vitamin D: It aids calcium absorption. Daily sun exposure is beneficial.
- Engage in physical activity: Exercise helps maintain bone strength.
- Take supplements with doctor's advice: If dietary intake is insufficient, calcium tablets can be taken under medical supervision.
Calcium deficiency is a "silent problem," gradually weakening the body from within. Ignoring minor symptoms like hair loss, muscle cramps, dry skin, or fatigue can have serious consequences. Therefore, timely assessment of your diet, consumption of calcium-rich foods, and consultation with a doctor when necessary are essential.















