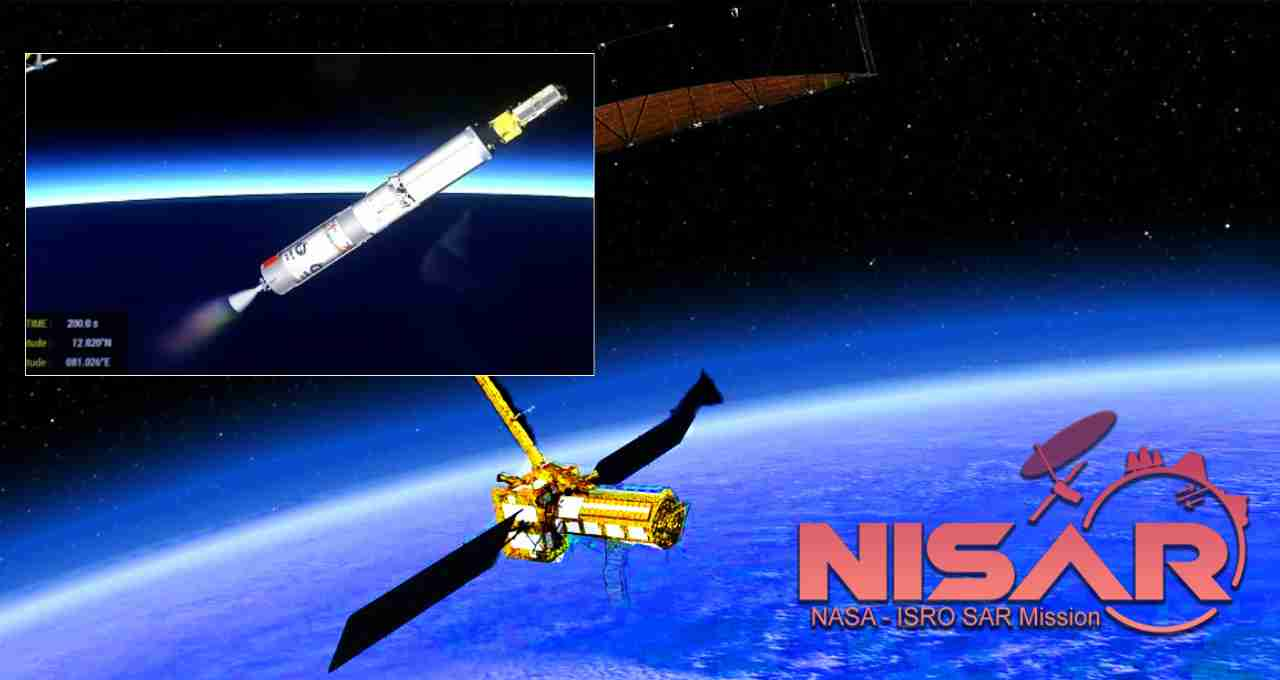
On July 30th, ISRO-NASA launched the NISAR satellite. This satellite will empower disaster management by providing accurate early warnings of earthquakes, tsunamis, and other natural disasters.
NISAR: On July 30, 2025, the joint ISRO and NASA satellite, NISAR, was successfully launched from Sriharikota. This satellite will monitor subtle changes on the Earth's surface, providing advance warnings of natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides. The launch, which coincided with an 8.8 magnitude earthquake in Kamchatka, Russia, underscored its necessity. For India, this satellite will play a crucial role in disaster management, agriculture, and water resource monitoring.
Successful Launch of NISAR from Sriharikota
On July 30, 2025, the NISAR satellite, jointly developed by ISRO and NASA, was successfully launched from India's Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, at 5:40 PM. The mission was placed in a Sun-Synchronous Orbit with the help of the GSLV-F16 rocket. This is the first time that the GSLV has sent a satellite into this orbit.
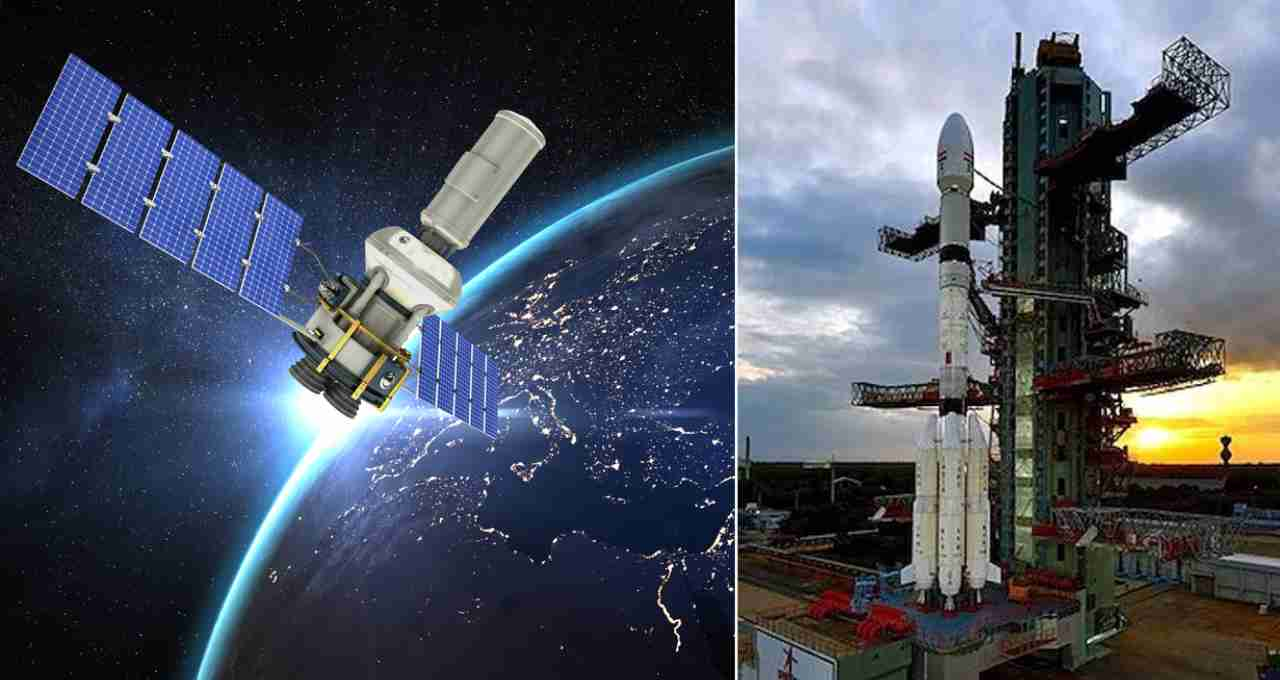
This satellite weighs approximately 2,400 to 2,800 kilograms and is about the size of an SUV. It is designed to observe the Earth's surface in all weather conditions, day and night, even through clouds.
Kamchatka Earthquake Highlights the Need for Warning Systems
On the same day as the NISAR launch, a massive earthquake of magnitude 8.8 struck near the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, in the Sea of Okhotsk. This earthquake triggered a tsunami warning in 12 countries, including Japan, Hawaii, California, Alaska, Chile, Peru, and New Zealand. Experts estimated the energy of the earthquake to be equivalent to 9,000 to 14,000 Hiroshima bombs.
Waves up to 5 meters high were observed on the Kuril Islands. In the Fukushima region of Japan, people were reminded of the devastating tsunami of 2011. This event made it clear that a large number of lives could be saved if warnings were issued in time. This is precisely what NISAR will do.
What is NISAR and How Will It Work?
NISAR stands for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar. It is an Earth Observation satellite equipped with two types of radar: L-band (developed by NASA) and S-band (developed by ISRO). With their help, it can record even the smallest changes on the Earth's surface.
This satellite will repeatedly image selected regions of the Earth. This will help detect any unusual movement or displacement on the surface of an area. These changes begin to appear before earthquakes or other disasters.
Early Warning of Earthquakes and Tsunamis

NISAR's greatest strength is its ability to identify signs of impending disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis ahead of time. The satellite's monitoring system will track subtle movements in the fault lines beneath the Earth's surface.
The satellite can also track disturbances on the ocean surface, changes in water levels, and wave patterns after an earthquake. This will allow for early warnings of potential tsunamis in coastal areas. Based on this warning, people can be evacuated to safe places in time.
Monitoring Volcanoes, Landslides, and Floods
NISAR is capable of identifying not only earthquakes but also hazards such as volcanic eruptions, landslides, and floods. When a volcano is about to erupt, the ground beneath it gradually swells. NISAR will be able to identify this.
Before a landslide, layers of soil slowly begin to shift. By accurately imaging mountainous areas, this satellite can provide these indications early on. Similarly, if the water level of rivers suddenly rises, it is a sign of flooding. NISAR will continuously monitor this as well.
How Important is This Mission for India?
India is geographically a disaster-sensitive country. The Himalayan region is always at risk of major earthquakes. Landslides in Uttarakhand, Himachal, and the Northeast, and floods in states like Assam and Kerala are common challenges. In such a situation, satellites like NISAR can prove to be a protective shield for India.
Use in Agriculture and Water Management
The use of NISAR will not be limited to disaster warnings. This satellite can also bring revolutionary changes in the field of agriculture. It can assess crop condition, soil moisture, and irrigation needs. It can also make a major contribution to water management. It will track groundwater levels, reservoir status, and river flow. This will help in dealing with the water crisis and creating better water policies.
Coastal Monitoring and Protection of the Marine Environment
A large part of India is surrounded by the sea. Coastal erosion, the strength of sea waves, sea ice, and environmental changes will be monitored by NISAR. This will make it possible to issue alerts in coastal areas in advance and save marine biodiversity.
What were the Technical Challenges in the Launch?
The NISAR mission was initially scheduled to launch in March 2024, but had to be postponed due to technical problems. The antenna of the L-band radar built by NASA was experiencing excessive heat. After successfully resolving this issue, it was launched on July 30, 2025.
Another major benefit of the NISAR mission is that its data will be free and public. Scientists, researchers, government institutions, and other agencies will be able to use this data to conduct better studies on natural disasters and environmental changes.