NASA is going to drop the International Space Station into the Pacific Ocean after 2030. This decision was made due to technical weaknesses and increasing costs. Now, research work will be conducted on private space stations.
International Space Station: NASA has made a major decision regarding the International Space Station (ISS). This space laboratory will no longer remain outside Earth's atmosphere; instead, it will be dropped into 'Point Nemo,' a remote location in the Pacific Ocean. Operating since 1998, this station has provided historic achievements for science and humanity. However, it has now reached the end of its lifespan, and maintaining it could prove to be not only risky but also extremely expensive.
What is the International Space Station?
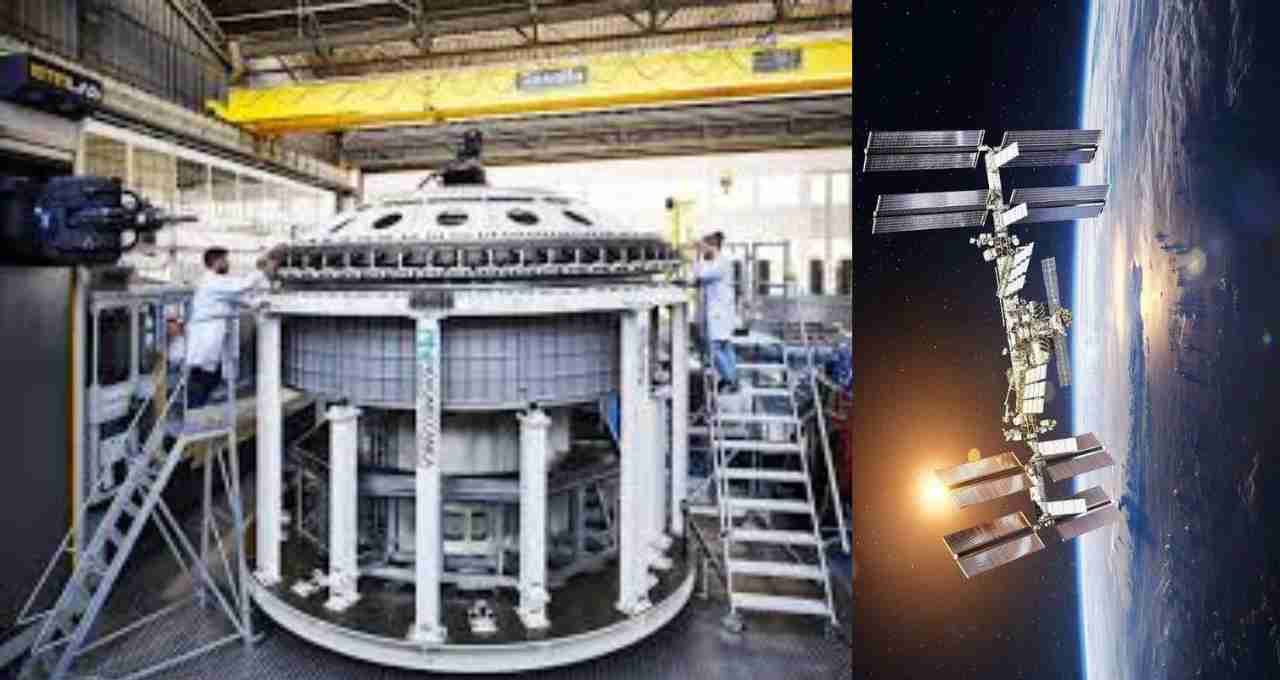
The ISS is a massive space laboratory located approximately 400 kilometers above the Earth's surface. It is about the size of a football field and weighs over 430 tons. The station orbits the Earth at a speed of 28,000 kilometers per hour. It is operated jointly by NASA, Russia's Roscosmos, the European Space Agency (ESA), Japan's JAXA, and the Canadian Space Agency.
More Than 280 Astronauts Have Visited So Far
The ISS began in 1998, and since then, more than 280 astronauts from 26 countries have visited. This station has witnessed numerous experiments in the fields of science, technology, and medicine. Research conducted in the unique microgravity environment has given a new direction to many areas on Earth.
Operation Will Become Risky After 2030
According to a NASA report, the ISS's primary structure is gradually weakening. Components such as modules, trusses, and radiators have now reached the end of their lifespan. After 2030, its operation will not only be fraught with risk, but its maintenance will also become extremely expensive.
Why Point Nemo is the Final Resting Place
NASA and its partners have chosen Point Nemo, the most isolated part of the Earth, to 'deorbit' the ISS. This location is in the South Pacific Ocean and is known as the "Spacecraft Cemetery." Neither humans live here nor birds fly. This location is 3,000 miles from New Zealand and 2,000 miles from Antarctica. This is why dropping spacecraft here is considered the safest.

SpaceX Will Build the Deorbit Vehicle
A special spacecraft, a deorbit vehicle, will be needed to bring the ISS toward Earth. This task has been assigned to SpaceX. This vehicle will take the ISS to Point Nemo in a controlled manner. With this, the 30-year journey of this space station will come to an end forever.
Were There No Options to Save It?
NASA considered several options before deciding to drop the ISS. The first idea was to push it into a higher orbit so that it could become a permanent historical relic. However, the risk of collision with debris would increase at a higher altitude, which could happen even once a year.
The second option was to disintegrate the ISS in place and bring its main parts to Earth for museums or research. However, this plan was extremely expensive and could have put the lives of astronauts at risk. Therefore, this option was also rejected.
NASA has also clarified that the fragments that remain after burning the ISS will be collected from the sea for research or disposal.










