Bakrid, also known as Eid-ul-Adha or Eid-ul-Zuha, is an important festival in Islam. This celebration transcends mere religious rituals; it carries a profound message of humanity, sacrifice, faith, and social service. In 2025, Bakrid will be observed on Saturday, June 7th. Let's explore the historical background of this festival, the significance of Qurbani (sacrifice), and its social and spiritual aspects.
Historical and Religious Background of Bakrid
According to Islamic tradition, Bakrid is directly linked to the trial of Hazrat Ibrahim (peace be upon him), where Allah tested his faith by commanding him to sacrifice his most beloved son. This was a significant ordeal for Hazrat Ibrahim. He accepted Allah's command without question and prepared his son, Ismail, for sacrifice.
Hazrat Ismail also accepted this command as the will of Allah. However, as Ibrahim was about to sacrifice his son, Allah, in a miracle, replaced Ismail with a lamb. This event became a symbol of faith, devotion, and sacrifice in Islamic history, and the tradition of Qurbani during Bakrid began.
The True Meaning of Qurbani: More Than Just Animal Sacrifice
There is often a misconception outside the Muslim community that Bakrid is merely a festival of animal sacrifice. However, the reality is far deeper and more humane. Qurbani signifies rising above self-interest, ego, and worldly attachments to completely surrender oneself to Allah's will. The Qurbani offered during Bakrid symbolizes that spiritual sacrifice where an individual prioritizes Allah's command above all else.
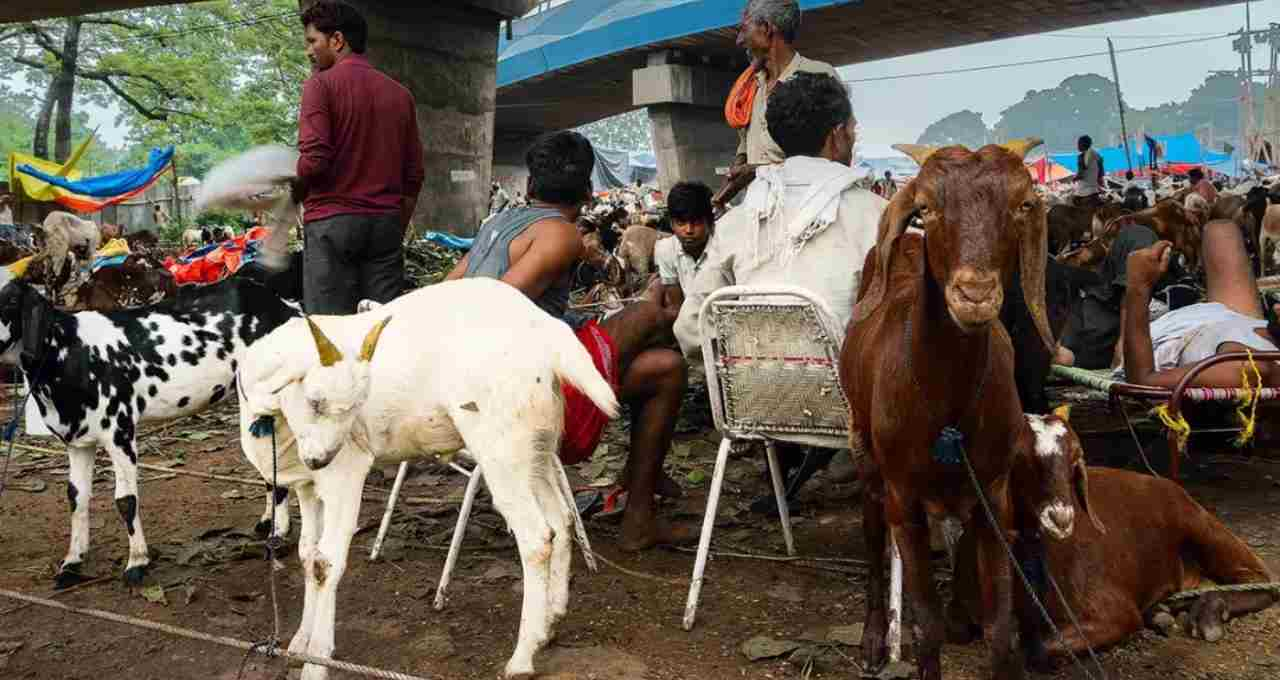
On this day, Muslims offer special prayers and then perform the halal sacrifice of a goat, sheep, cow, or camel. This sacrificed meat is divided into three parts: one for themselves, one for relatives and friends, and one for the poor and needy. This distribution strengthens the spirit of equality, brotherhood, and cooperation within society.
The Deep Connection Between Qurbani and Social Service
Bakrid is not just a religious festival; it is also a symbol of social equality and service. When the meat from the Qurbani reaches every section of society, it highlights the fundamental Islamic principle that "every human being is equal." This festival teaches that it is not only our duty to feed our families but also to alleviate the hunger of the needy.
In today's world, where society appears divided along lines of class, caste, and religion, the message of Bakrid becomes even more relevant: humanity comes first.
The Interrelation of Hajj and Bakrid
Another significant aspect of Bakrid is its connection to Hajj. Hajj is one of the five pillars of Islam, and it is obligatory for every able Muslim to perform Hajj in Mecca once in their lifetime. During the Hajj pilgrimage, Qurbani is also performed, recalling the tradition of Hazrat Ibrahim. Thus, both Bakrid and Hajj emphasize sacrifice, devotion, and genuine faith in Allah.
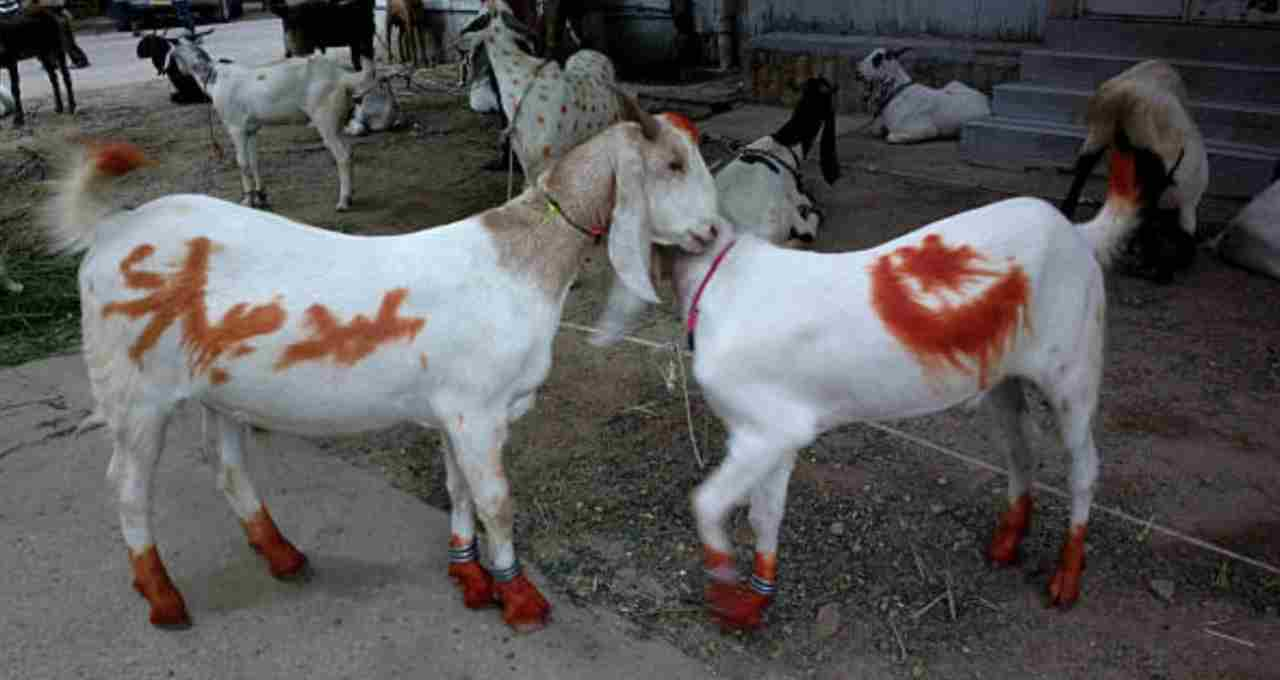

Bakrid's Message in Modern Society
In today's self-centered world, Bakrid teaches us that the greatest sacrifice is the one made for the benefit of others. By embracing this message of sacrifice and service, we can not only become better individuals but also establish a ber and more harmonious society. Bakrid also teaches that religion is not merely ritualistic but a way of life that inspires humility, generosity, and compassion.
The Festivities: A Confluence of Tradition and Modernity
On the morning of Bakrid, special Eid prayers are offered. People wear new clothes, embrace each other, and exchange Eid greetings. Special dishes are prepared at home, and relatives, friends, and the poor are invited for meals. This festival serves as a vibrant example of social harmony and togetherness.















