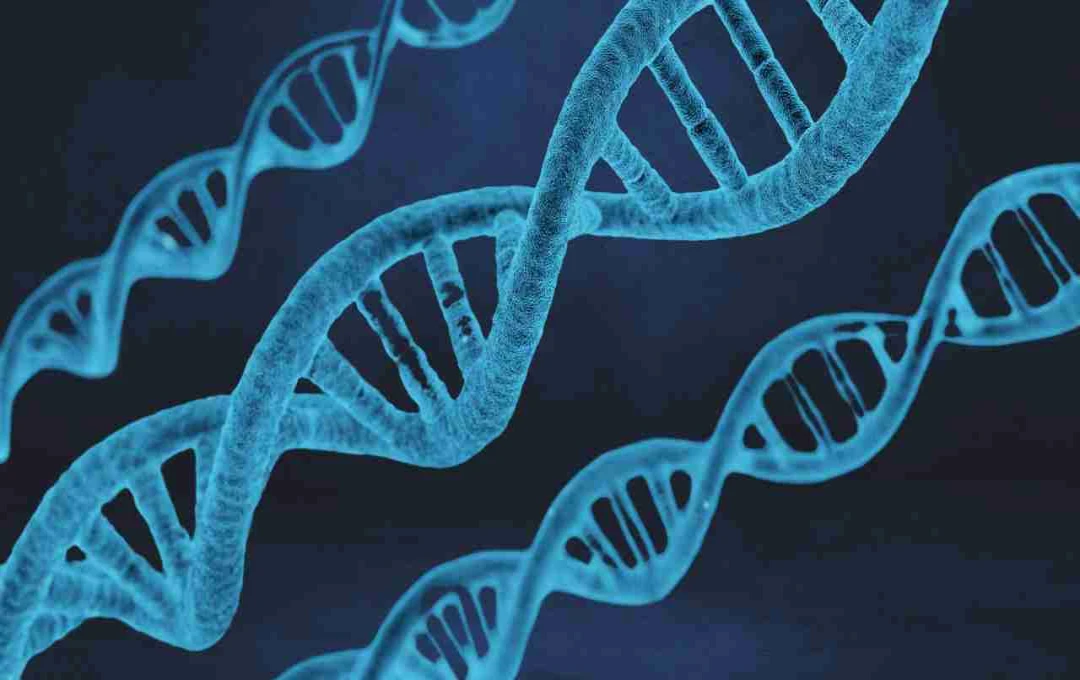
Numerous mental health disorders, such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Autism Spectrum Disorder, and anxiety, have long been the subject of scientific research. However, a recent international study confirms that not only external factors but also our genes—our genetic makeup—play a significant role in these disorders. This study delves into why even identical twins raised in similar environments may exhibit differences in mental health traits.
What is unique about this research?
This study was conducted by King's College London, a prestigious institution in the United Kingdom, in collaboration with 23 universities worldwide. It combined data from approximately 21,792 identical twins from 11 separate studies. This makes it the largest genetic research study on twins to date, known as a Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS).
What are the research findings?
The researchers identified specific genetic variants that determine a person's environmental sensitivity. This sensitivity dictates how much and what kind of impact a given situation or experience will have on an individual.
For example, if two children experience the same type of stress, it doesn't necessarily mean both will be affected equally. One child might remain unaffected, while the other might develop depression or anxiety. This difference, it is now believed, could be due to differences in their genes.
How are genetic sensitivities linked to mental health problems?

The research found that certain genes involved in neurodevelopment, immune function, and the central nervous system play a role in traits like autism. Other genes affect hormones that regulate stress response, contributing to variations in symptoms like depression or anxiety.
A significant finding was that genes controlling catecholamines, hormones impacting psychosis, were also identified.
Environmental Sensitivity: Not everyone reacts the same way
The research found that certain genetic variants determine how we react to our environment—such as stress, social pressure, and emotional experiences. In other words, the same experience can have different effects on two different people, and their genes may be the reason.
Dr. Elham Asari, the study's lead postdoctoral researcher, explains, "Every individual's response to experiences is different. Our findings show that specific genes determine how much an experience will impact mental health."
Why is this research important?

This research not only provides a better understanding of mental health but could also revolutionize future treatment and counseling methods. If a child is identified as genetically more sensitive, then:
- They can be protected from stressful environments.
- Specialized counseling or therapy can be arranged.
- Medication and treatment can be chosen based on individual sensitivity.
- Behavioral understanding can be developed within the school and family.
Awareness is crucial for mental health
In today's world, where mental stress is becoming a common problem among children and adults alike, it's crucial to understand that circumstances are not the sole cause. Genes, inherited from birth, often profoundly affect how we process experiences. Therefore, considering an individual's genetic background and sensitivity before making any decisions in the mental health field has become essential.
The Way Forward: What could change in the future?
- Future genetic screening could identify a child or individual's susceptibility to various mental disorders.
- Personalized medicine and psychotherapy will be based on genes, not just behavior.
- Educational and parenting methods can be adapted to better support sensitive children.
- Awareness about mental disorders will increase, reducing the stigma.
This study reveals that mental health is not solely a consequence of life's difficulties but is deeply connected to our internal bodily structure. If we use this information correctly, we can not only prevent millions from mental illnesses but also help them lead better, more understanding, and balanced lives.