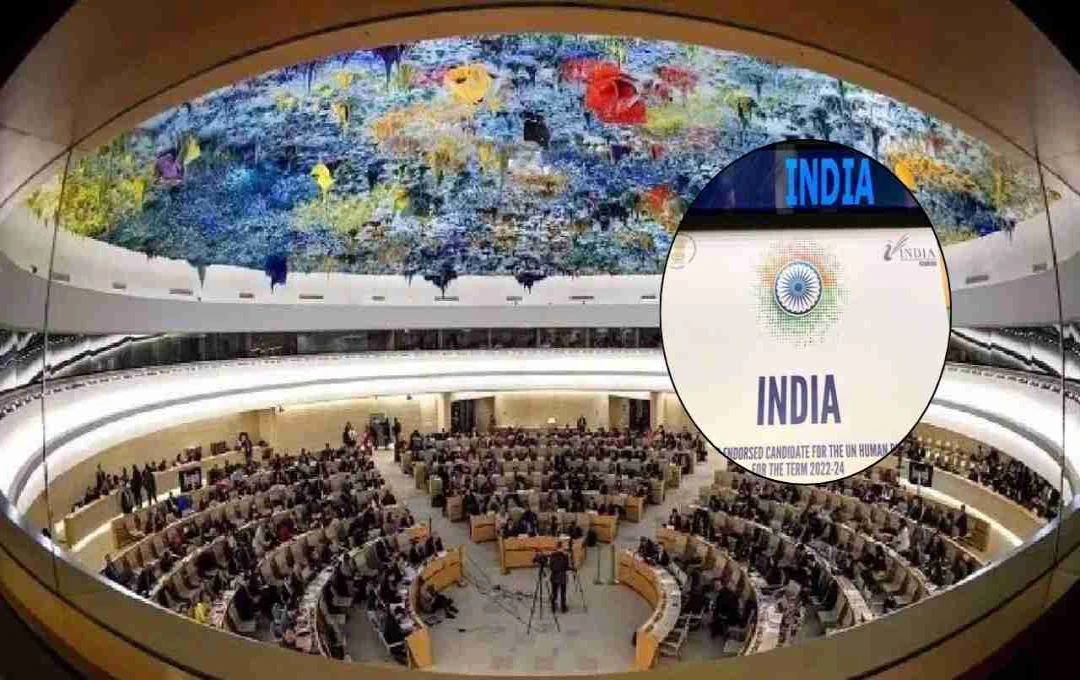
India has been elected to the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) for the 2026-28 term for the seventh time. India's priorities will include the protection of human rights, fundamental freedoms, and the promotion of women's and children's rights.
New Delhi: India has been elected for the 2026-28 term of the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC). This marks India's seventh term, reflecting its commitment to human rights and fundamental freedoms. The UNHRC announced the results of the election held on Tuesday, which showcased India's consistent support and global recognition.
Beginning of the Term
India's three-year term will commence on January 1, 2026. India's Permanent Representative to the United Nations, Parvathaneni Harish, stated that this election is not only a symbol of honor but also a testament to India's commitment on the global stage. He thanked all delegations for their support and underscored India's unwavering role in upholding human rights.
Structure of the United Nations Human Rights Council
The UNHRC comprises a total of 47 member states. These countries are elected for a three-year term by the UN General Assembly under equitable geographical distribution rules. The primary objective of the Council is the protection, monitoring, and preservation of human rights. India has consistently been an active member and has maintained continuity in its role.

India's History in the UNHRC
India has been a member of the Council since its formation in 2006. In the first election, India received 173 out of 190 votes, which was the highest. Subsequently, India was also a member during 2006-2007, 2008-2010, 2012-2014, 2015-2017, 2019-2021, and 2022-2024. India was not a member of the Council only in 2011, 2018, and 2025. Thus, this seventh term holds special significance for India.
Other Elected Member States
The UNHRC has also released a list of other member states elected for the term commencing January 1, 2026. These include Angola, Chile, Ecuador, Egypt, Estonia, Iraq, Italy, Mauritius, Pakistan, Slovenia, South Africa, the United Kingdom, and Vietnam. These countries will work as India's collaborators in the Council on global human rights issues.
India's Priorities
India's priorities in the Council will include the protection of human rights, support for the rights of developing countries, and the promotion of fundamental freedoms. India will also prioritize women's rights, children's rights, and safety in the digital world. Thus, India will play an active role in global issues within the Council.