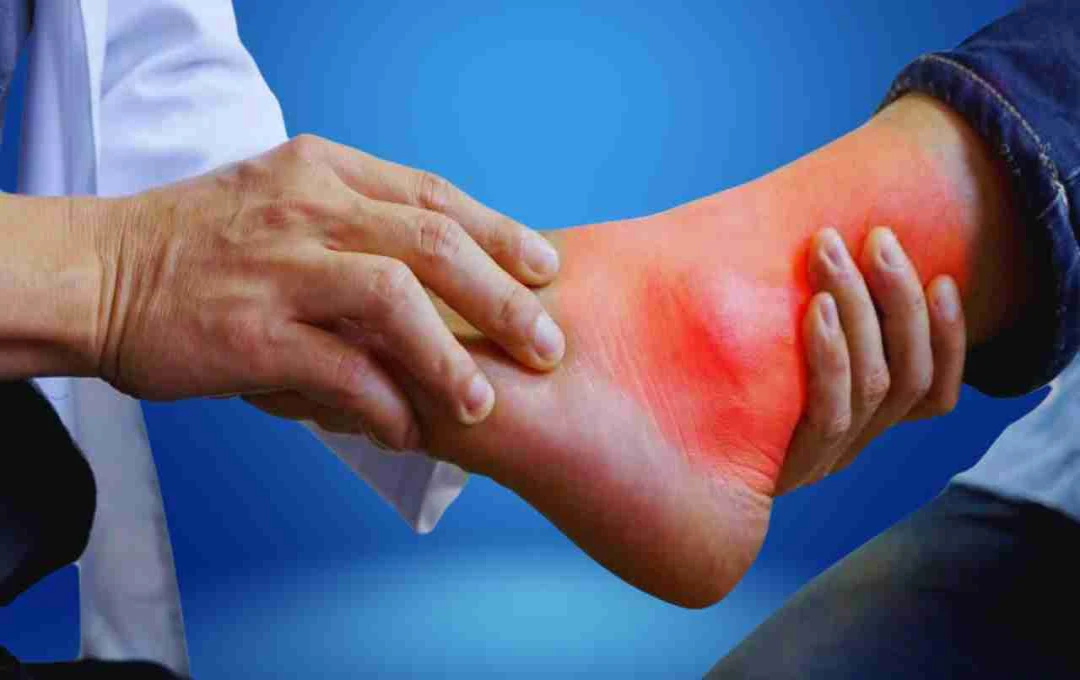
Uric acid problems are increasingly prevalent among women today. It's often believed to be a primarily male issue, but research shows it's becoming quite common in women as well. Symptoms like joint and ankle pain, swelling, and difficulty moving may indicate elevated uric acid levels. This article will delve into the reasons for increased uric acid in women, its causes, and how it can be managed.
What is Uric Acid?
Uric acid is a chemical produced in the body when purines, substances found primarily in protein-rich foods like meat, fish, and lentils, are broken down. During digestion, uric acid is formed. Normally, it travels through the bloodstream to the kidneys and is excreted through urine. However, when uric acid production increases or excretion is hindered, it accumulates in the blood, forming crystals in the joints and causing problems like gout.
Why is Uric Acid a Greater Problem in Women?

Several factors contribute to higher uric acid levels in women compared to men, including hormonal changes, digestive function, and lifestyle.
1. Impact of Hormonal Changes
Sex hormones, particularly estrogen, play a crucial role in regulating uric acid levels in women. Estrogen aids in uric acid excretion. However, estrogen levels decrease, especially during menstruation and after menopause, leading to increased uric acid levels.
- Hormonal imbalances during menstruation can exacerbate uric acid problems.
- Post-menopausal estrogen deficiency increases uric acid levels, making women more susceptible to conditions like gout.
2. Poor Digestion and Metabolism
Women often experience more digestive problems, hindering the body's ability to properly digest proteins and purines. Metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and liver and kidney diseases also affect uric acid levels. A weakened digestive system contributes to uric acid accumulation.
3. Fasting and Irregular Eating Habits
In many cultures, women frequently observe fasts or alter their diets during religious observances. This impacts metabolism and reduces the production of digestive enzymes. A deficiency in these enzymes affects protein digestion, leading to elevated uric acid levels.
Normal Uric Acid Levels
Normal uric acid levels in women are considered to be between 2.4 and 6.0 mg/dL. Levels exceeding this range are termed hyperuricemia, a major cause of gout and joint pain.
Persistent joint pain, swelling, or difficulty moving could indicate rising uric acid levels. It's crucial to get a blood test and consult a doctor promptly.
Main Causes of Increased Uric Acid in Women

- Hormonal Imbalance: Estrogen deficiency increases uric acid.
- Weak Digestive System: Poor digestion prevents the body from properly breaking down purines.
- Lifestyle Changes: Irregular eating habits, fasting, or dieting affect metabolism.
- Chronic Diseases: Diabetes, liver disease, and kidney problems contribute to increased uric acid.
- Stress and Mental Pressure: Stress causes hormonal changes that impact uric acid.
What to Do About Elevated Uric Acid?
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Avoid high-protein foods, red meat, alcohol, and fried foods. Consume plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, and leafy greens.
- Drink Enough Water: Drink at least 2-3 liters of water daily to help excrete uric acid through urine.
- Exercise Regularly: Yoga, walking, and light exercise improve metabolism.
- Consult a Doctor: Get a blood test for uric acid levels and follow your doctor's advice on medication.
- Take Precautions During Fasting: Avoid prolonged fasting; eat small, frequent meals.
Women often attribute joint and ankle pain to aging or fatigue, but it can be a sign of elevated uric acid. Hormonal changes, digestive problems, and unhealthy lifestyles exacerbate uric acid issues in women. Don't ignore this problem; get regular health checkups. A balanced diet and a regular lifestyle can significantly help prevent this problem.